White Paper: Data Center Power Usage
Power Monitoring and Metering:
How Understanding Power Consumption Can Lead to a More Efficient Data Center
A White Paper by Raritan
Download PDF

Overview
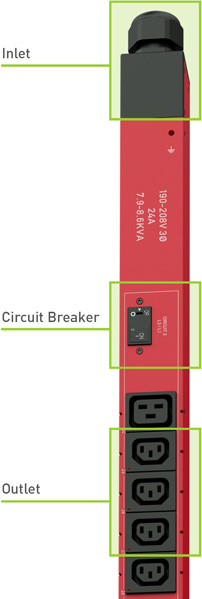
If you are a data center manager, you are continuously faced with the challenge of providing increased power levels in progressively reduced areas. You must meet these challenges all while adhering to budget constraints, maintaining mission-critical uptime and reliability, and reducing the stress on existing data center infrastructures. This demanding challenge is only made possible by properly monitoring power at the outlet, circuit breaker, and inlet levels.
Unfortunately, far too many businesses opt for data center solutions that use outdated power monitoring that cannot provide power efficiency insights, alerts, and fail-safes needed to create a scalable, reliable, and agile IT infrastructure. Thankfully, in 2019, Green Grid introduced Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) to use as a benchmark for measuring and reporting energy efficiency and data center productivity. PUE is a ratio of the amount of power needed to operate and cool the data center vs. the amount of power drawn by the IT equipment in the data center. This ratio tells you how much of your data center’s energy is used by its IT equipment and how much is overhead. But without appropriately measuring and monitoring power consumption, you will not be able to measure the overall efficiency of your data center.
This white paper addresses how power monitoring solutions can be effectively used throughout the data center to meet demands, while simultaneously delivering an IT environment that achieves evolving business, usage, regulatory, energy efficiency, and financial goals.
Where To Measure Power Consumption
In every data center there are several key locations where power usage can and should be measured. A failure to accurately measure power data in the following locations can result in unplanned outages, reduced operating efficiencies, and higher costs.
1. Power Entering The Data Center. In a stand-alone structure, incoming energy is typically measured from the utility electrical service entrance that feeds all the electrical and mechanical equipment used to power, cool, and condition the building. However, far too often, data centers are located on a floor within a multi-purpose building. In the latter instances, a utility submeter should be installed on the floor housing the data center to accurately measure the total power consumed.
2. Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS). The UPS should be measured. In instances where the UPS only provides power to IT equipment, then it can be used as the denominator for the necessary PUE calculation. With this in mind, it is imperative to note that the UPS might also be providing power to the data center's rack-based cooling equipment, which means that additional considerations must be made before it can be used in a PUE calculation.
3. Panel and Floor Measurements. Floor-mounted power distribution units (PDUs) provide a crucial management bridge between a building's primary power and various equipment racks within a data center. Each floor PDU can handle larger amounts of energy than an ordinary power strip and typically provides power to multiple equipment racks. Because of this, consumption measurements should also be calculated here to give a view of the accumulated energy as it steps down through the power chain.
4. Rack-based Power Measurements. The best place to meter power at the rack is through metered or switched rack power distribution units (PDUs).
5. Individual Outlet Measurements on the Rack PDU. The power used at the respective outlets of a rack PDU should also be measured. Intelligent rack PDUs can be used to monitor the power consumption at the outlet level to increase efficiencies and improve uptime.

How is Power Data Gathered in a Data Center?
Measuring and monitoring power data are vital to the overall IT health of a data center. Without these essential measurements, data centers are more susceptible to higher levels of outages, increased downtime, higher costs, and in some instances potential damage to the existing IT infrastructure. Data centers can instead deploy the following solutions to effectively monitor power consumption at the outlet, circuit breaker, and inlet levels to avoid these issues.
Basic Rack PDUs
Basic rack PDUs are an affordable and proven technology. They are typically power strips constructed from high-quality components and can be used to support the correct voltage and current distribution to several outlets at once. The downside of a basic rack PDU is that it doesn't have the instrumentation needed to provide valuable power monitoring insights. Additionally, basic PDUs cannot be remotely managed.
Intelligent Rack PDUs
An intelligent rack PDU is a device that features remote accessibility and management. It provides power monitoring at both the rack PDU level and the individual outlet level. Additionally, it offers specific user-defined threshold alerts to more effectively monitor your entire data center from on-site or remote locations. These highly customizable power monitoring devices also feature remote power on/off capabilities, outlet level switching, real-time environmental data analysis, and the ability to be easily integrated with existing directory servers.
There are four typical types of intelligent rack PDUs that can assist you with data center power monitoring.
1. Metered Inlet Rack PDUs. This intelligent PDU measures power consumption at the inlet level to help determine power usage and the available capacity of the circuits feeding the rack, making it easier to provision equipment. You can avoid overloading circuits and easily calculate efficiency metrics. The data gathered can be displayed locally and over a secure network.
2. Metered Outlet Rack PDUs. This intelligent PDU features the same capabilities as a metered inlet rack PDU while also providing metering at the outlet level. Like metered inlet rack PDUs, outlet-metered models determine power usage, available capacity at the rack, and eases provisioning. Most importantly, outlet-level metering allows you to understand power consumption at the device or server level, making it possible to compare efficiencies and allocate costs to specific business units or data center customers. Once again, the gathered data can be displayed locally and over a secure network.
3. Switched Rack PDUs. This intelligent PDU features the same capabilities as a metered inlet rack PDU while enabling authorized users to securely power-cycle outlets from remote locations. Through remote power-cycle, energy can be conserved, devices can be rebooted more quickly and effectively, services can be efficiently restored in an outage, unauthorized device provisioning is prevented, and inrush currents are minimized.
4. Switched Rack PDUs With Outlet Metering. This intelligent PDU combines all the capabilities of switched and outlet metered rack PDUs. It is the most comprehensive type of intelligent rack PDU and can be used to help effectively reduce costs and maximize energy efficiencies across devices. It offers the best outlet power measurement and control for rack-level monitoring.
For most data centers, intelligent rack PDUs are the optimal power monitoring solution to reduce costs, increase energy efficiencies, improve availability, and manage the existing capacity of the entire data center.
Branch Circuit Monitors and Individual Device Load Measurement
Branch circuit monitors are pivotal to effectively measuring power consumption across the data center. Typically, these electrical devices are designed to measure the current load for each circuit on a designated electrical panel. The device collects and reports electrical capacity and power usage data and alerts operators when the current load is approaching the breaker's designated rating. This heightened level of power monitoring is critical in data centers where additional servers can accidentally be plugged into a circuit close to its designated operating capacity. Finally, branch circuit monitors can be used to continuously measure current across circuits, so that trips, outages, and overloads can be avoided, and the optimal levels of uptime can be enjoyed.
Overhead Busway Systems
Overhead busway systems are an alternative to panels to deliver power. They move power cabling up and out of the floor and run it overhead, primarily using the same conduit or flexible whip system. Monitoring solutions can also be used in conjunction with busway system to help provide operators with exact power usage. All too often, when new equipment is added to a rack, the cable ratings can be exceeded, which can trip circuit breakers and cause unexpected power outages. Fortunately, an overhead busway system is designed to provide power feed monitoring in real-time so that you can more effectively plan to install new equipment at the rack level. This heightened level of monitoring can also help you ensure that the data center's electrical system is properly balanced across phases so that increased savings and energy efficiencies can be enjoyed.
What Other Factors Contribute to Power Consumption in the Data Center?
Environmental Sensors
Another major contributor to power consumption in a data center is its HVAC system, which can sometimes be overlooked but have a crucial role in energy consumption. That is why it is essential to have environmental sensors deployed throughout your data center. There are sensors for determining temperature and humidity, the difference in air pressure between two locations, the rate of airflow and the presence of particles within it, the presence of water, and more.
At their core, environmental sensors are designed to improve power efficiency. These sensors can be placed at the bottom, middle, and top portions of racks on the cool air inlet side to ensure that IT equipment is cooled to the appropriate levels. When IT equipment is overcooled, it can consume additional power, but it can increase operating costs without providing any additional benefit. Thus, environmental sensors play a key role in providing power monitoring solutions to reduce the overall operating costs within a data center.
What Benefits Does Power Monitoring Deliver Within a Data Center?
By using the correct power monitoring tools in your data center, you can enjoy lower operating costs, reduce unexpected outages, optimize device power consumption, and manage the entire data center more effectively. In this vein, you must take the time needed to install devices that can monitor power at the outlet, circuit breaker, and inlet levels. Additionally, individual devices should be monitored regularly to ensure that peak periods are not accidentally overlooked. Through individual device power consumption data, you will be able to more effectively configure racks so that the equipment power consumption patterns complement each other and thus avoid tripping a breaker, while simultaneously maintaining the optimal load levels.
As part of your power monitoring solutions, you should leverage intelligent rack PDUs to power your IT equipment. As was discussed previously within this white paper, these PDUs have the unique capability to effectively measure power consumption at the inlet and individual outlet levels. As part of these capabilities, intelligent rack PDUs can provide kilowatt usage data combined with CPU utilization data to determine which individual servers can handle additional capacity. These insights are needed to improve overall data center efficiencies through the effective redeployment or decommissioning of servers.
Finally, intelligent rack PDUs combined with environmental sensors can provide the power monitoring solutions needed to improve server uptime, reduce overheating (and overcooling), and provide a complete picture regarding the airflow in and around each server. The latter power data insights are essential to increasing uptime, reducing outages, and lowering operating costs.

Conclusion
Metering at the inlet, outlet, and circuit levels is vital to determine the power usage across an entire data center. Metering at the inlet level helps you effectively determine the power usage and available capacity of a rack, but it can reduce the risk of overloading circuits. Inlet level power monitoring also allows you to calculate energy efficiency efforts. Metering at the rack PDU circuit breaker levels is crucial to achieving an early warning system. This type of power monitoring provides you with alerts to avoid tripping a circuit breaker. It also provides the information necessary to effectively reduce power demands (when the circuit breaker is at lower usage levels). Metering at the outlet level helps you determine the rack's power usage and available capacity, but can also provide vital insights into the power consumption levels at the device and/or server level. The latter insights are key to identifying underutilized servers, allocating costs, and identifying ghost servers.
In conclusion, you can more effectively run a data center through the proper power monitoring tools. By accurately identifying servers that are running too hot or too cold, you can more readily save energy, avoid server crashes, redeploy or decommission servers, balance power usage (across servers and the entire data center), and identify opportunities to change or grow. In this vein, through the right combination of tools, you can more effectively measure and understand power data to increase the effectiveness of IT operations and the allocation of resources.
To learn more about how power monitoring solutions can be effectively leveraged at the inlet, outlet, and circuit breaker levels, visit the Raritan PX Intelligent Rack PDUs website.
About Raritan
Raritan began developing KVM switches for IT professionals to manage servers remotely in 1985. Today, as a brand of Legrand, we are a leading provider of intelligent rack PDUs. Our solutions increase the reliability and intelligence of data centers in the top 10 Fortune 500 technology companies. Learn more at Raritan.com
Download PDF